Mind in Motion: How Exercise Boosts Mental Health and Wellbeing

We’re all aware of the importance of exercise in maintaining our physical health. However, its profound effect on mental wellbeing often goes unnoticed. Studies show that regular physical activity can reduce stress, anxiety, and depression. That’s because when you exercise, your brain releases endorphins—those feel-good signals that act as natural mood lifters. And if you needed another reason to lace up those gym shoes, consider that physical activity also promotes better sleep, heightens cognitive function, and enhances self-esteem, all culminating in a healthier, happier you.
Looking for ways to experience that mind-body connection? Here are some tips to kickstarting a fitness routine that will boost your total wellbeing in no time.

Starting Small: Baby Steps Toward a Healthier Mind
Embarking on a new exercise routine can feel daunting, especially if you’re not accustomed to being active. But remember: every journey begins with a single step. Start small by incorporating short bursts of activity into your day. Take the stairs at work instead of the elevator, go for a brisk walk during your lunch break, or try out a beginner’s yoga class. The key is to find activities that you enjoy and that fit into your lifestyle. By gradually building up your exercise routine, you’ll soon reap the mental rewards of your efforts.
Community Connection: Finding Support in Movement
Exercise doesn’t have to be a solo endeavor. In fact, joining a fitness class or a recreational sports team can amplify exercise’s mental health benefits by providing a sense of camaraderie and belonging. Many workplaces sponsor recreational sports leagues, such as volleyball or kickball, that their employees can join. Surrounding yourself with like-minded individuals who share your passion for movement can be incredibly motivating and uplifting. Whether you’re high fiving your workout buddy after a challenging gym session or sharing post-exercise endorphin highs with your teammates, the sense of community that comes with group exercise can be a powerful antidote to feelings of isolation or loneliness.
Finding Your Sweat Therapy
So what’s the best kind of exercise? The one you’ll actually do! Explore different activities and find the one that works for your lifestyle and preferences. Love channeling your inner calm? Give yoga or Pilates a try. Need to blow off some steam? Kickboxing might be your jam. Are you a nature enthusiast? Maybe hiking or kayaking is the thing for you. The key is to find an activity that resonates with you and moves your body in a way that feels enjoyable. To turn up the fun factor even more, create an upbeat playlist to instantly make any workout more invigorating.

Establish a Routine That Sticks
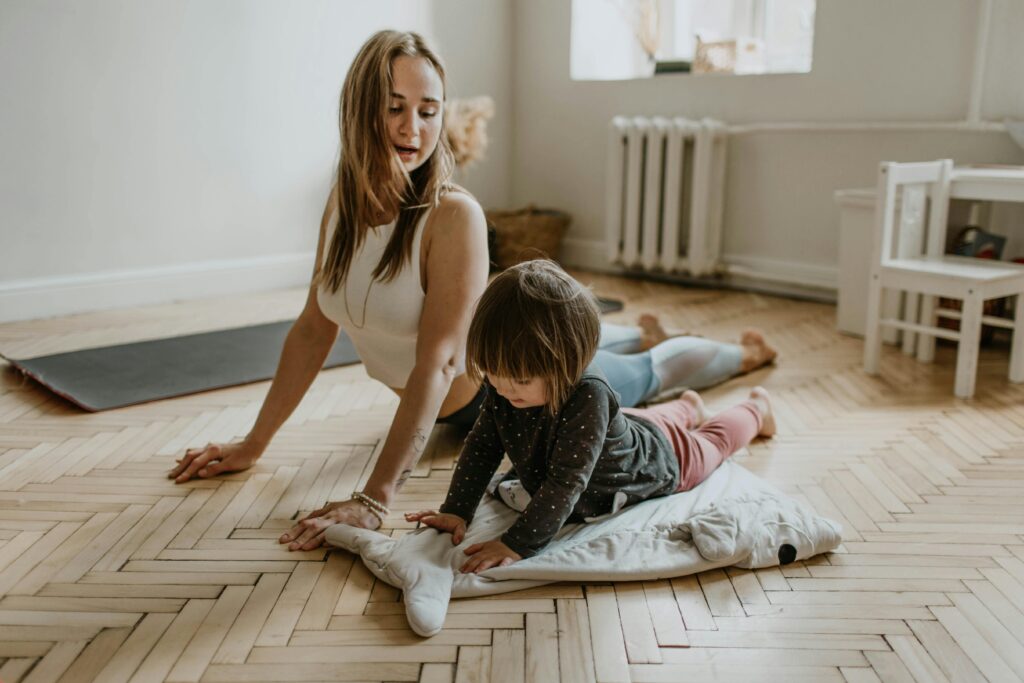
While the mental health perks of exercise are compelling, consistency is key to reaping the benefits long-term. Aim to incorporate physical activity into your weekly routine, whether it’s a daily walk after work, weekend hikes, or dance parties with your kids in the living room. Setting a recurring schedule makes it more likely that exercise will become an ingrained habit. Lay out your workout clothes or pack your gym bag the night before to remove any barriers in the morning. Recruit a friend or family member to join the fun—having an accountability partner can make a world of difference.
As you dive into your exercise journey, remember: progress over perfection. Some days you might crave an intense sweat session, while other days, simply moving your body mindfully is good enough. Exercise is about much more than burning calories or clocking time at the gym. The goal isn’t to push yourself to exhaustion, but rather, to foster a lifestyle of joyful movement that you look forward to. Over time, this self-care ritual will become second nature.
Whether you’re seeking stress relief, a mood boost, or simply a way to quiet your mind, exercise offers a holistic path to improved mental wellbeing. So get ready to incorporate exercise into your routine and move your way to a healthier version of you.